
Unit #6. The 8D Solving Process Model
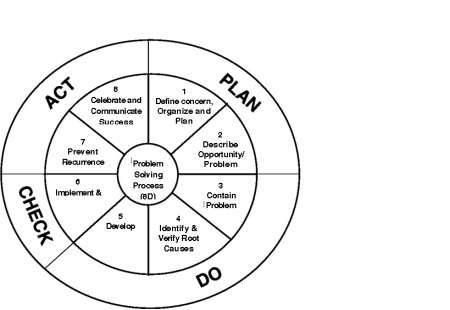 The Reactive Problem Solving Process
The Reactive Problem Solving Process
What is it?
The Reactive Problem Solving Process Is a systematic process that describes, analyzes, and subsequently uncovers the root cause(s) of the problem. It is used to solve “past” actions that are now causing unwanted effects. Generally, it takes more time, energy, and resources to correct a problem than to prevent it. Problem Solving is a reactive process utilized
by an individual or team for describing a problem, finding its root cause(s), and implementing corrective action/solution.
When to use it?
- When there is a gap between the current state and the documented standard
- When the product does not meet the requirements of the print or the specifications
- When the process is out of control
- When the customers require evidence of problem resolution
Reactive Problem Solving or Proactive Continuous Improvement: Which One?
Using a systematic approach to solve problems can help groups and individuals avoid some of the common pitfalls of ineffective problem solving.
The benefits of this approach:
- Effectively analyzes all aspects of the problem before developing a conclusion
- Gathers all critical data, either about the problem or about proposed corrective actions/solutions
- Tackles problems that are within the control of group members
- Works on problems that are specific, manageable, and well defined
- Develops satisfactory rationale for a corrective action/solution
- Involves critical people – especially those outside the group – when looking for corrective actions/solutions
- Plans how to implement completely and evaluate the recommended corrective action/solution successfully
| 8D Step | Issues To Be Addressed | Expansion/Divergence | ||
|
• | What is our problem topic or
opportunity? |
• • |
What is wrong with what?
Identify potential problem topics or |
| • | What is our objective? | opportunities. | ||
| • | Who do we need to work on the
problem? |
• | Develop list of potential problem
solving team members. |
|
| • | What is our project plan? | |||
| • | What will our meeting and decision‑
making process be? |
|||
|
• | What do we want to change? | • | Lots of problem statements for
consideration. |
|
• | What interim containment actions may be implemented to isolate the customer from the problem? | • | Brainstormed list of potential interim
actions for containment.
|
| • | Are we following the standards? | were produced using the process | ||
| • | What is the implementation plan for
containment? |
and that may be defective.
|
||
| • | Were the interim action(s)
successful? |
could cause a similar defect in
this product. |
||
|
||||
|
• | What’s preventing us from reaching | • | Lots of potential causes generated. |
| Root Causes | the “desired state”? | • | Lots of potential corrective | |
| • | How could we reach the “desired
state”? |
actions/solutions generated. | ||
|
• | What’s the best corrective action/ | • | Lots of criteria for evaluating potential |
| Action Plan | solution (or set of actions)? | corrective actions/solutions. | ||
| • | What’s the best plan for
implementation? |
• | Lots of ideas on how to implement
and evaluate the selected corrective action(s)/solution(s) |
|
|
• | Will the corrective
action(s)/solution(s) help us reach the “desired state”? |
||
|
• | Are we following the plan? | • | Other applicable processes/tools. |
|
• | How do we recognize contributions? | • | Many recognition plans identified. |
| • | Is this a new Best Practice that | • | Many plans for communication | |
| should be shared with others? | identified. | |||
| • | Who should be informed of the
outcome of the corrective action(s)/solution(s)? |
|||
| • | How do we communicate successes
and future opportunities? |
Leave a comment